The so-called nail fungus (onychomycosis) is one of the most common dermatological infectious diseases and at the same time one of the most difficult to treat. The absence of obvious symptoms of infection in the initial stages of the disease is the reason for the late diagnosis of onychomycosis and, as a result, delays in treatment.
types of mushrooms
Onychomycosis is caused by pathogenic fungi of the genus Trichophyton, which penetrate the tissues of the nail plate and nail bed, gradually destroying them and causing negative changes in local immunity.
Depending on the clinical manifestations of nail fungus, three forms of the disease are distinguished:
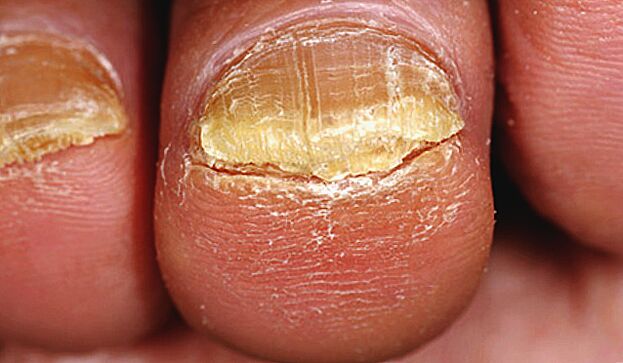
- Normotrophic – in this case, the nail plate retains its normal thickness, but is painted in colors unusual for a healthy nail (cloudy white, yellow-gray, gray-brown, etc. ).
- The hypertrophic form is characterized by excessive thickening of the nail, rising above the surface of the nail bed and greatly protruding beyond its borders. Often with this form, deformation of the plate is observed - it becomes pronounced bumpy, grows in width and causes pain when walking, as it grows into soft tissues.
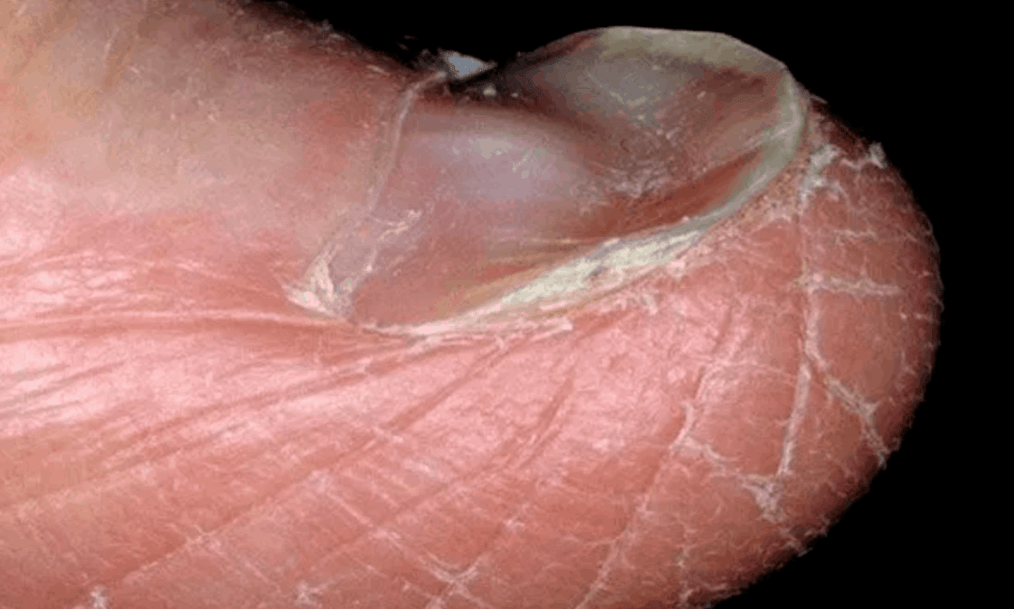
- The atrophic form is manifested by thinning of the nail, which acquires a dull color (sometimes with gray-yellow spots, streaks or "bubbles"). It is important to remember that only a specialist knows how to spot toenail fungus. Getting rid of advanced nail fungus without surgery will be very difficult.
If you find signs of fungus on your nails, hands or other formations, you should urgently seek advice from a dermatologist.
symptoms
Manifestations of onychomycosis can be divided into three groups, which differ depending on the severity of damage to the nail plate.
- I direct (initially). At this stage of the development of the disease, the nail retains its normal thickness and color, but its surface becomes dull and loses its shine. The cuticles and skin around the nail can appear overly dry and calloused quickly. At the same time, scaly spots in the interdigital spaces and itching of different strengths can be observed - from light and episodic to strong and permanent.
- II. Stage (developed). In the second stage, visible signs of infection appear on the nail. The nail plate begins to thicken, but at the same time it becomes brittle - when cutting the nail it is obvious that it "crumbles", leaving uneven edges at the cutting point. White, yellow, gray or brown spots or stripes appear on the nail, and theSurface of the nail acquires an uneven relief, thickening of the nail can develop to such an extent that any manipulation (manicure, pedicure) causes pain to a person, at this stage there is an unpleasant odor from the affected nails (especially with onychomycosis on the legs), which cannot be eliminated with the help of hygiene measures.
- Tier III (Hard). At this stage of onychomycosis, the nail completely loses its functions and properties, and the fungal infection spreads to the nail fold and soft tissues under the nail. This stage is most often characterized by the death of the nail and its loss.
Causes of the fungus
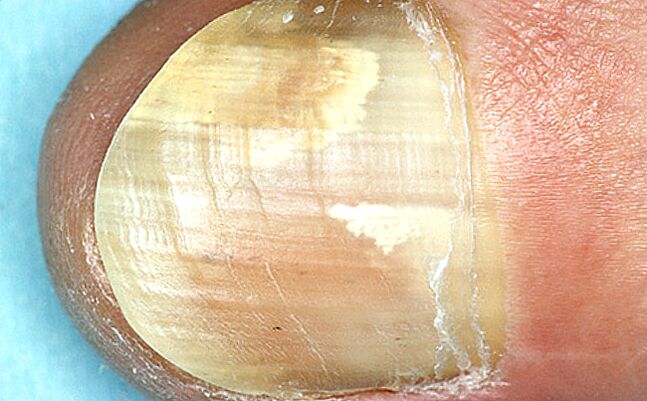
There is only one reason for onychomycosis: infection with pathogenic fungi and their growth and reproduction in the tissues of the nails.
But the fungus, which is almost ubiquitous, only affects some people. The reason for this is simple: infection requires not only a pathogen, but also conditions that favor infection.
These include:
- Decreased local immunity. Skin and nails have their own resources to prevent infection. But when wearing tight and uncomfortable shoes, frequent or regular skin injuries, too thorough and deep pedicure / manicure, contact with aggressive substances, the protective functions of the skin and nails are weakened, which facilitates the penetration of the fungus and its reproduction.
- Occupational or daily activities that involve prolonged exposure of hands/feet to wet environments. This does not have to involve direct contact with water or other liquids - wearing rubber shoes and gloves creates warm, humid conditions that are favorable for pathogenic fungi.
- Non-compliance with the rules of personal hygiene provokes subungual fungus. Unfamiliar footwear, lack of individual shoes when visiting public swimming pools and saunas, prematurely changing stockings and socks for fresh ones, etc.
Nail fungus: treatment
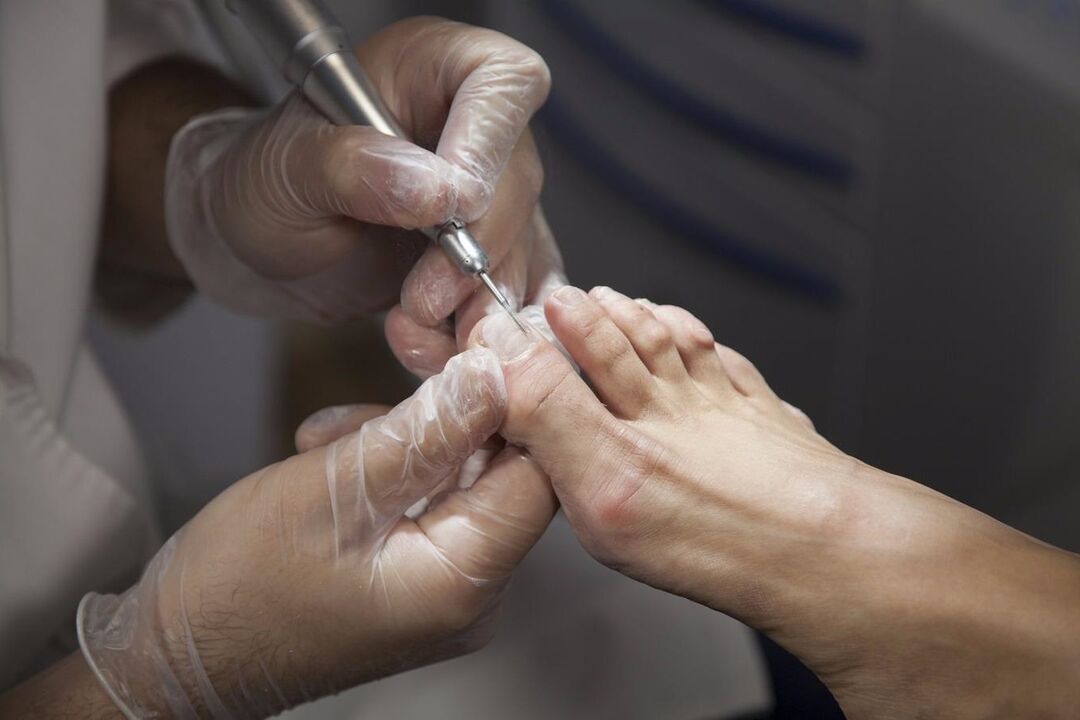
The treatment of onychomycosis is complicated by the peculiarities of the nails themselves, the density of which does not allow medicinal substances to penetrate into their deep layers.
Therefore, in the case of fungal infections of the nails, an artificial nail thickness reduction with the help of special nail files is often carried out. As a result, the surface of the nail plate is freed from the most dense outer layer, which increases the ability of the active ingredients of the drugs to penetrate deep into them.
With a deep lesion of the nail involving the tissues of the nail bed, it is advisable to surgically remove the nail plate, which is performed under local anesthesia. After that, treatment is prescribed according to the severity of the disease.
To date, the only way to get rid of onychomycosis is to use drugs from the group of antifungal drugs. These drugs have a selective effect on pathogenic fungi, stopping their activity and reproduction, causing the death of pathogens.
Depending on the extent to which the fungus has spread to the area surrounding the nail and whether the pathogen has entered the bloodstream, systemic antifungal drugs for oral administration or topical agents (ointments, creams, solutions) can be prescribed.



















